Antonia Colibasanu
A war of words has troubled Moldova for more than two weeks. It started when Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy warned of a Russian coup plot against Moldova on Feb. 10. Two days later, Moldovan President Maia Sandu said that Ukraine sent intelligence to her government, according to which the Russians had a plan to destabilize the country by organizing protests and by employing “violent actions.” It would have been the perfect cover for inciting a coup in a country that is prone to violent protest-induced governmental change.
In fact, Moldova had been on high alert even before Zelenskyy’s warnings. Earlier this month, Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov – in a not-so-veiled threat – accused the West of “having its sights” on Moldova as a country that might “follow Ukraine’s path.” Even before that, Sandu enraged Moscow in January by implying Moldova might consider joining NATO. Two influential Russian lawmakers responded by saying Moldovan membership in NATO could lead to the country’s destruction. Following the threat, Sandu requested that the parliament pass draft legislation to provide the Prosecutor’s Office and the State Information System with tools to combat risks and threats to the country’s security more effectively.
News of the coup added to the already high anxiety in Moldova and triggered a change in government. Prime Minister Natalia Gavrilita resigned and was replaced by Sandu’s security adviser and National Security Council secretary – a signal that the government was prepared to operate from a mandate to protect Moldova from Russian threats. This is no small thing for a country usually committed to a policy of neutrality. Sandu and the new prime minister promptly issued statements on the shortcomings of neutrality and a potential constitutional change to join a “larger alliance” – that is, NATO.
These kinds of statements, meanwhile, have stirred up domestic partisan activity. Pro-Russia factions are expected to object, while nationalist factions seek to double down on their own agenda, which includes petitions to the EU to add Moldovan oligarchs and other sympathetic politicians to sanctions lists.
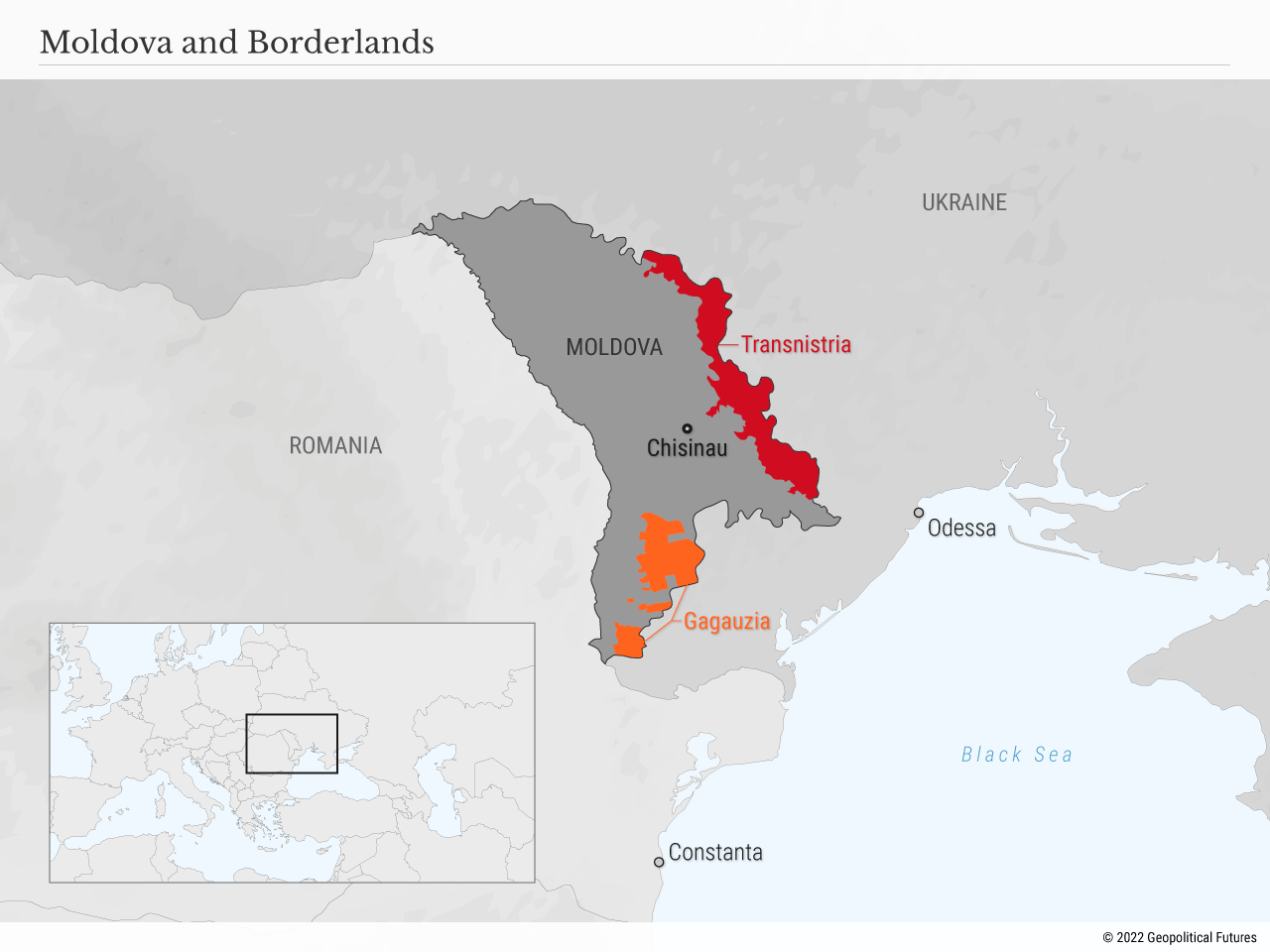
Moscow has responded to Moldova in kind. On Feb. 21, President Vladimir Putin canceled a 2012 foreign policy decree that committed Moscow to peacefully resolving the border crisis of Transnistria. The region is a narrow strip of land in eastern Moldova that has been controlled by a Russian-backed government since a war in 1992 fought between Transnistrian separatists and Moldova. And for 30 years, some 2,000 Russian soldiers have been stationed there. (The separatist region is said to host the largest weapons depot in Europe – about 20,000 tons of ammunition and military equipment, albeit likely from the Soviet era.) In 2012, Moscow agreed to help find a way to peacefully resolve the conflict, but that was at a time when Russia was seeking closer relations with the EU and the U.S. Clearly, that is no longer the case. In other words, Transnistria is a European region in which Russia has citizens to protect and military assets already in place to protect them.
This is why fears are well-founded that Russia’s escalation in Ukraine could embroil Moldova. And it explains the most recent exchanges between Russia, Ukraine and Moldova. On Feb. 23, Russia’s Defense Ministry claimed that Ukraine was planning an operation to invade Transnistria. Moldovan media reported that the claim was merely Russian psyops. Still, Kyiv went out of its way to say it would act to help Moldova if Russia ever attacked.
These statements paint a picture of escalation that Russia would benefit from. Moscow’s frontal attacks in Ukraine haven’t been especially successful, so logic dictates the execution of a flanking maneuver. Belarus – helmed by a staunchly pro-Russia government – and Moldova are the only places in which Russia could launch such a maneuver. The cancellation of the Moldova decree, then, is meant to force Moldova to accept Russian dominance and influence. It does not indicate an attack, but it does make it clear that one is a very real possibility.
Imagine a scenario in which Moldova got militarily involved in the Ukraine war and opened a second front. Considering how quickly Kyiv responded to a potential Russian threat in Moldova, Ukraine could spare some soldiers along with weapons they received from the West to fight in Ukraine. This would allow Kyiv to ask for even more Western help. The U.S. and its allies may not want the conflict to escalate further – in fact, NATO has already urged Ukraine to use its arsenal for defensive operations, not for offensive ones – but if Moldova were attacked, and if Ukraine rushed to its aid, they would have little choice but to continue their support.
For Russia, sustaining an offensive in both eastern Ukraine and southern Ukraine, where the country borders Transnistria, would be a logistical nightmare. Opening a new front might be worth the effort so long as it doesn’t spread itself too thin, doesn’t lose territory it has gained, and doesn’t upset the U.S. so much that it needs to intervene directly. Ideally, it would lead to negotiations. The fact that U.S. President Joe Biden mentioned Moldova in a recent speech in Warsaw shows that a new front is the last thing Washington wants. With that in mind, Russia may determine it is better served by opening a new front in Belarus rather than Moldova. If Russia dominates Moldova, it would imperil NATO’s southern reach, and would thus draw in the United States. Belarus would be easier to ignore.
Meanwhile, the tension inside Moldova has benefited its pro-Europe governing party. The coup rumors helped Sandu and her party consolidate their position. Had it not been for the warning Ukraine delivered to Moldova, Sandu’s government would have likely fallen by the end of the month due to protests driven by general discontent with the country’s poor economic performance. Installing a new government during what appears to be a security crisis has allowed Sandu to avoid further political instability.
The mere prospect of a Russian threat against Moldova allowed the government to establish better relations with the West, giving Sandu direct access to Western leaders like Biden with whom she met during his visits to Munich and Warsaw. Engaging with the U.S. and EU leaders directly makes it more likely for Moldova to obtain security guarantees and funding to improve its economy. Moreover, Russia’s cancellation of the 2012 decree has freed Moldova up from the negotiation process Russia had forced it into. De facto, the negotiating format set forth by the decree was already doomed; Russia’s invasion of Ukraine essentially put an end to the “5+2” setup in which Moscow and Kyiv, in addition to the Organization for Security and Economic Cooperation in Europe, sat next to each other as “mediators” and “guarantors” vis-a-vis Chisinau and Tiraspol, with the United States and European Union reduced to “observers.” It could no longer function, and Moscow’s cancellation only confirmed as much. If anything, through this cancellation Russia acknowledged its weakened position.
For Ukraine, the situation in Moldova buys much-needed time. It could help Kyiv negotiate more help from the West, and it could forestall another Russian offensive. It’s possible that none of this will come to pass, but the potential can’t be ruled out. For Russia, opening a new front, either in Belarus or Moldova, would give it a strategic advantage. If current anxieties lead to the destabilization of either country, Poland or Romania could be next.
No comments:
Post a Comment